本文是基于BeeHive版本1.6.0进行分析。
BeeHive核心思想涉及两个部分:
各个模块间从直接调用对应模块,变成以Service的形式,避免了直接依赖。
App生命周期的分发,将耦合在AppDelegate中的逻辑拆分,每个模块以微应用的形式独立存在。
Core+Plugin的形式可以让一个应用主流程部分得到集中管理,不同模块以plugin形式存在,便于横向的扩展和移植。
本文会按照以下顺序进行介绍:
BeeHive概览
BeeHive的架构图如下所示:
图中的BHContext,包含BeeHive的配置文件,提供全局统一上下文信息。
图中的BHCore包含:
BeeHive,提供组件库对外接口
BHModuleManager和BHModuleProtocol,注册和创建Module逻辑
BHServiceManager和BHServiceProtocol,注册和创建Service逻辑
BHRouter
Module、Service注册和调用逻辑只和核心模块相关,Module之间没有直接的关联关系。
对于Module和Service的注册,BeeHive提供了三种不同的形式:静态plist,动态注册,annotation。Module、Service之间没有关联,每个业务模块可以单独实现Module或者Service的功能。
图中包含了主要的BeeHive启动过程以及Module注册的时序逻辑。Module的事件分发源于BHAppDelegate中的triggerEvent 。
加载Module:
BeeHive.plist中配置的module和service是在 AppDelegate中调用 [[BeeHive shareInstance] setContext:[BHContext shareInstance]]; 时加载。
Module的实现中 +load内部调用 [BeeHive registerDynamicModule:[self class]]; 动态加载。
Module的实现中使用注解: @BeeHiveMod(XXModule)
BHAppDelegate中除了回调系统的事件,还将App生命周期进行扩展,增加ModuleSetup ,ModuleInit ,ModuleSplash ,此外开发人员还可以自行扩展。
扩展周期过程中,同时加入Module分析量化功能,每个模块Init的耗时均可计算出来,为性能优化做到数据上的支持。一个App的业务增多过程中,通过分析定位Module的Init耗时可以确定需要优化的Module。
Module遵循BHModuleProtocol 后,能够捕获App状态的回调,并拥有App生命周期内的全局上下文,通过context可获取配置参数,模块资源以及服务资源。
以BeeHive作为底层框架的App,除了解耦带来的便利,开发人员在开发新App过程中涉及相同功能的Module,无需重复造轮子,直接移植Module,开发一个App如同拼装积木,能组合需要的功能业务。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 BHModuleManager.m: //BHModuleInfos: [{moduleClass:String, ModuleLevel:NSNumber, modulePriority:String}] //BHModules: [id<BHModuleProtocol>] @interface BHModuleManager() @property(nonatomic, strong) NSMutableArray *BHModuleDynamicClasses; @property(nonatomic, strong) NSMutableArray<NSDictionary *> *BHModuleInfos; @property(nonatomic, strong) NSMutableArray<id<BHModuleProtocol>> *BHModules; @property(nonatomic, strong) NSMutableDictionary<NSNumber *, NSMutableArray<id<BHModuleProtocol>> *> *BHModulesByEvent; @property(nonatomic, strong) NSMutableDictionary<NSNumber *, NSString *> *BHSelectorByEvent; @end
BHModuleInfos 和BHModulesByEvent 中id<BHModuleProtocol>均按照moduleInstances 的moduleLevel 和modulePriority 进行了排序。
上图中包含注册静态plist中service的相关逻辑,App启动时通过BeeHive的setContext:来触发plist中service的注册。service的注册并没有创建对应的service实例,只是在BHServiceManager中建立Service协议 和实现该协议的类 之间的映射关系。
上图中是动态注册service的逻辑,这是在App启动事件分发时触发。Module根据需求动态注册某个服务,通常,注册service的代码在module的modInit:或者modSetup:中。
业务组件可以通过createService:直接调用服务。Service的调用和实现,核心是BHServiceManager。可以单独创建Services Interface Pod,统一放置要用的Services,这样的业务依赖就从网状式变成中心式,业务方只需依赖Services一个。
Service可以按需加载,BeeHive逻辑是将基础服务注册在plist中,业务型服务允许Service不先注册,直到业务需要时才被动态注册。
Service支持两种不同模式:
单例: 对于全局统一且无状态服务,建议使用这种创建形式,这样有利于Service的统一管理以及减少不必要内存消耗。
多实例: 每次调用服务都重新创建新的服务,对于涉及状态以及状态变化的服务最适合使用多实例方式。
在多线程环境下遇到了Service读写问题,已通过Lock来已避免Array crash问题。 不过Service还存在如下问题:
Service依赖关系,导致底层依赖的Service没有被创建时就被调用。
规划Service、Module创建顺序,使得App达到秒开,优化性能体验。
前者依赖问题计划通过调度机制来解决,后者还需要将AppDelegate更多业务剥离以及实践才可。
BeeHive使用createService:和createService:withServiceName:来创建实现了协议的对象,并且缓存该对象。
BeeHive模块生命周期事件
BeeHive会给每个模块提供生命周期事件,用于与BeeHive宿主环境进行必要信息交互,感知模块生命周期的变化。
事件分为三种类型:
在BHModuleManager的头文件中,Event的类型定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 typedef NS_ENUM(NSInteger, BHModuleEventType) { BHMSetupEvent = 0, BHMInitEvent, BHMTearDownEvent, BHMSplashEvent, BHMQuickActionEvent, BHMWillResignActiveEvent, BHMDidEnterBackgroundEvent, BHMWillEnterForegroundEvent, BHMDidBecomeActiveEvent, BHMWillTerminateEvent, BHMUnmountEvent, BHMOpenURLEvent, BHMDidReceiveMemoryWarningEvent, BHMDidFailToRegisterForRemoteNotificationsEvent, BHMDidRegisterForRemoteNotificationsEvent, BHMDidReceiveRemoteNotificationEvent, BHMDidReceiveLocalNotificationEvent, BHMWillPresentNotificationEvent, BHMDidReceiveNotificationResponseEvent, BHMWillContinueUserActivityEvent, BHMContinueUserActivityEvent, BHMDidFailToContinueUserActivityEvent, BHMDidUpdateUserActivityEvent, BHMHandleWatchKitExtensionRequestEvent, BHMDidCustomEvent = 1000 };
系统事件
系统事件通常是Application生命周期事件,例如WillResignActiveEvent , DidEnterBackgroundEvent , WillEnterForegroundEvent , DidBecomeActiveEvent , WillTerminateEvent 。
一般做法是使用BHAppDelegate来接管系统事件,如下所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 //TestAppDelegate.h #import "BeeHive.h" @interface TestAppDelegate : BHAppDelegate <UIApplicationDelegate> //TestAppDelegate.m - (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions { [BHContext shareInstance].application = application; [BHContext shareInstance].launchOptions = launchOptions; [BHContext shareInstance].moduleConfigName = @"BeeHive.bundle/BeeHive";//可选,默认为BeeHive.bundle/BeeHive.plist [BHContext shareInstance].serviceConfigName = @"BeeHive.bundle/BHService"; [BeeHive shareInstance].enableException = YES; [[BeeHive shareInstance] setContext:[BHContext shareInstance]]; [[BHTimeProfiler sharedTimeProfiler] recordEventTime:@"BeeHive::super start launch"]; [super application:application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:launchOptions]; ... return YES; }
在BHAppDelegate的实现文件中,实现了一系列的系统调用事件。如下所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 - (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions { [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMSetupEvent]; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMInitEvent]; dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMSplashEvent]; }); #if __IPHONE_OS_VERSION_MAX_ALLOWED >= 100000 if ([UIDevice currentDevice].systemVersion.floatValue >= 10.0f) { [UNUserNotificationCenter currentNotificationCenter].delegate = self; } #endif #ifdef DEBUG [[BHTimeProfiler sharedTimeProfiler] saveTimeProfileDataIntoFile:@"BeeHiveTimeProfiler"]; #endif return YES; } #if __IPHONE_OS_VERSION_MAX_ALLOWED >= 80400 -(void)application:(UIApplication *)application performActionForShortcutItem:(UIApplicationShortcutItem *)shortcutItem completionHandler:(void (^)(BOOL))completionHandler { [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.touchShortcutItem setShortcutItem: shortcutItem]; [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.touchShortcutItem setScompletionHandler: completionHandler]; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMQuickActionEvent]; } #endif - (void)applicationWillResignActive:(UIApplication *)application { [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMWillResignActiveEvent]; } - (void)applicationDidEnterBackground:(UIApplication *)application { [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMDidEnterBackgroundEvent]; } - (void)applicationWillEnterForeground:(UIApplication *)application { [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMWillEnterForegroundEvent]; } - (void)applicationDidBecomeActive:(UIApplication *)application { [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMDidBecomeActiveEvent]; } - (void)applicationWillTerminate:(UIApplication *)application { [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMWillTerminateEvent]; } - (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application openURL:(NSURL *)url sourceApplication:(NSString *)sourceApplication annotation:(id)annotation { [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.openURLItem setOpenURL:url]; [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.openURLItem setSourceApplication:sourceApplication]; [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.openURLItem setAnnotation:annotation]; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMOpenURLEvent]; return YES; } #if __IPHONE_OS_VERSION_MAX_ALLOWED >= 80400 - (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)app openURL:(NSURL *)url options:(NSDictionary<NSString *,id> *)options { [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.openURLItem setOpenURL:url]; [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.openURLItem setOptions:options]; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMOpenURLEvent]; return YES; } #endif - (void)applicationDidReceiveMemoryWarning:(UIApplication *)application { [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMDidReceiveMemoryWarningEvent]; } - (void)application:(UIApplication *)application didFailToRegisterForRemoteNotificationsWithError:(NSError *)error { [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.notificationsItem setNotificationsError:error]; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMDidFailToRegisterForRemoteNotificationsEvent]; } - (void)application:(UIApplication *)application didRegisterForRemoteNotificationsWithDeviceToken:(NSData *)deviceToken { [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.notificationsItem setDeviceToken: deviceToken]; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMDidRegisterForRemoteNotificationsEvent]; } - (void)application:(UIApplication *)application didReceiveRemoteNotification:(NSDictionary *)userInfo { [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.notificationsItem setUserInfo: userInfo]; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMDidReceiveRemoteNotificationEvent]; } - (void)application:(UIApplication *)application didReceiveRemoteNotification:(NSDictionary *)userInfo fetchCompletionHandler:(void (^)(UIBackgroundFetchResult))completionHandler { [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.notificationsItem setUserInfo: userInfo]; [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.notificationsItem setNotificationResultHander: completionHandler]; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMDidReceiveRemoteNotificationEvent]; } - (void)application:(UIApplication *)application didReceiveLocalNotification:(UILocalNotification *)notification { [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.notificationsItem setLocalNotification: notification]; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMDidReceiveLocalNotificationEvent]; } #if __IPHONE_OS_VERSION_MAX_ALLOWED >= 80000 - (void)application:(UIApplication *)application didUpdateUserActivity:(NSUserActivity *)userActivity { if([UIDevice currentDevice].systemVersion.floatValue >= 8.0f){ [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.userActivityItem setUserActivity: userActivity]; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMDidUpdateUserActivityEvent]; } } - (void)application:(UIApplication *)application didFailToContinueUserActivityWithType:(NSString *)userActivityType error:(NSError *)error { if([UIDevice currentDevice].systemVersion.floatValue >= 8.0f){ [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.userActivityItem setUserActivityType: userActivityType]; [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.userActivityItem setUserActivityError: error]; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMDidFailToContinueUserActivityEvent]; } } - (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application continueUserActivity:(NSUserActivity *)userActivity restorationHandler:(void (^)(NSArray * _Nullable))restorationHandler { if([UIDevice currentDevice].systemVersion.floatValue >= 8.0f){ [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.userActivityItem setUserActivity: userActivity]; [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.userActivityItem setRestorationHandler: restorationHandler]; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMContinueUserActivityEvent]; } return YES; } - (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application willContinueUserActivityWithType:(NSString *)userActivityType { if([UIDevice currentDevice].systemVersion.floatValue >= 8.0f){ [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.userActivityItem setUserActivityType: userActivityType]; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMWillContinueUserActivityEvent]; } return YES; } - (void)application:(UIApplication *)application handleWatchKitExtensionRequest:(nullable NSDictionary *)userInfo reply:(void(^)(NSDictionary * __nullable replyInfo))reply { if([UIDevice currentDevice].systemVersion.floatValue >= 8.0f){ [BeeHive shareInstance].context.watchItem.userInfo = userInfo; [BeeHive shareInstance].context.watchItem.replyHandler = reply; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMHandleWatchKitExtensionRequestEvent]; } } #endif #if __IPHONE_OS_VERSION_MAX_ALLOWED >= 100000 - (void)userNotificationCenter:(UNUserNotificationCenter *)center willPresentNotification:(UNNotification *)notification withCompletionHandler:(void (^)(UNNotificationPresentationOptions options))completionHandler { [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.notificationsItem setNotification: notification]; [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.notificationsItem setNotificationPresentationOptionsHandler: completionHandler]; [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.notificationsItem setCenter:center]; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMWillPresentNotificationEvent]; }; - (void)userNotificationCenter:(UNUserNotificationCenter *)center didReceiveNotificationResponse:(UNNotificationResponse *)response withCompletionHandler:(void(^)())completionHandler { [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.notificationsItem setNotificationResponse: response]; [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.notificationsItem setNotificationCompletionHandler:completionHandler]; [[BeeHive shareInstance].context.notificationsItem setCenter:center]; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] triggerEvent:BHMDidReceiveNotificationResponseEvent]; }; #endif @end
这样所有的系统事件都可以通过BHModuleManager的triggerEvent:来处理。
在上述事件中,BHMInitEvent 和BHMTearDownEvent 事件需要做特殊处理。
先看看BHMInitEvent 的处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 - (void)handleModulesInitEventForTarget:(id<BHModuleProtocol>)target withCustomParam:(NSDictionary *)customParam { BHContext *context = [BHContext shareInstance].copy; context.customParam = customParam; context.customEvent = BHMInitEvent; NSArray<id<BHModuleProtocol>> *moduleInstances; if (target) { moduleInstances = @[target]; } else { moduleInstances = [self.BHModulesByEvent objectForKey:@(BHMInitEvent)]; } [moduleInstances enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(id<BHModuleProtocol> moduleInstance, NSUInteger idx, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) { __weak typeof(&*self) wself = self; void ( ^ bk )(void); bk = ^(){ __strong typeof(&*self) sself = wself; if (sself) { if ([moduleInstance respondsToSelector:@selector(modInit:)]) { [moduleInstance modInit:context]; } } }; [[BHTimeProfiler sharedTimeProfiler] recordEventTime:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ --- modInit:", [moduleInstance class]]]; if ([moduleInstance respondsToSelector:@selector(async)]) { BOOL async = [moduleInstance async]; if (async) { dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ bk(); }); } else { bk(); } } else { bk(); } }]; }
BHMInitEvent 事件是触发各个module启动时的初始化逻辑。这里从self.BHModulesByEvent中取出BHMInitEvent 事件对应的module数组,遍历其中的每个module实例,向其发送modInit:消息。这里会考虑是否异步执行module的初始化。如果moduleInstance重写了async方法,那么就会根据该方法的返回值来决定是否异步执行module的初始化。
modInit:方法由各个module实例各自实现,可以在其中注册一个外部模块可以访问的Service接口。
1 2 3 4 5 -(void)modInit:(BHContext *)context { //注册模块的接口服务 [[BeeHive shareInstance] registerService:@protocol(UserTrackServiceProtocol) service:[BHUserTrackViewController class]]; }
再看看BHMTearDownEvent 事件。这个事件中可以处理module的清理工作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 - (void)handleModulesTearDownEventForTarget:(id<BHModuleProtocol>)target withCustomParam:(NSDictionary *)customParam { BHContext *context = [BHContext shareInstance].copy; context.customParam = customParam; context.customEvent = BHMTearDownEvent; NSArray<id<BHModuleProtocol>> *moduleInstances; if (target) { moduleInstances = @[target]; } else { moduleInstances = [self.BHModulesByEvent objectForKey:@(BHMTearDownEvent)]; } //Reverse Order to unload for (int i = (int)moduleInstances.count - 1; i >= 0; i--) { id<BHModuleProtocol> moduleInstance = [moduleInstances objectAtIndex:i]; if (moduleInstance && [moduleInstance respondsToSelector:@selector(modTearDown:)]) { [moduleInstance modTearDown:context]; } } }
由于module具有优先级,且self.BHModulesByEvent结构中,每种事件类型对应的modules数组中的module元素都已经按照优先级从高到低排列,因此逆序对modules数组中的module元素调用modTearDown:方法。
通用事件
在系统事件的基础之上,扩展了应用的通用事件,例如modSetup 、modInit 等,可以用于编码实现各插件模块的设置与初始化。
扩展的通用事件如下:
所有的事件都可以通过调用BHModuleManager的triggerEvent:来处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 - (void)triggerEvent:(NSInteger)eventType { [self triggerEvent:eventType withCustomParam:nil]; } - (void)triggerEvent:(NSInteger)eventType withCustomParam:(NSDictionary *)customParam { [self handleModuleEvent:eventType forTarget:nil withCustomParam:customParam]; } - (void)handleModuleEvent:(NSInteger)eventType forTarget:(id<BHModuleProtocol>)target withCustomParam:(NSDictionary *)customParam { switch (eventType) { case BHMInitEvent: //special [self handleModulesInitEventForTarget:nil withCustomParam :customParam]; break; case BHMTearDownEvent: //special [self handleModulesTearDownEventForTarget:nil withCustomParam:customParam]; break; default: { NSString *selectorStr = [self.BHSelectorByEvent objectForKey:@(eventType)]; [self handleModuleEvent:eventType forTarget:nil withSeletorStr:selectorStr andCustomParam:customParam]; } break; } } - (void)handleModuleEvent:(NSInteger)eventType forTarget:(id<BHModuleProtocol>)target withSeletorStr:(NSString *)selectorStr andCustomParam:(NSDictionary *)customParam { BHContext *context = [BHContext shareInstance].copy; context.customParam = customParam; context.customEvent = eventType; if (!selectorStr.length) { selectorStr = [self.BHSelectorByEvent objectForKey:@(eventType)]; } SEL seletor = NSSelectorFromString(selectorStr); if (!seletor) { selectorStr = [self.BHSelectorByEvent objectForKey:@(eventType)]; seletor = NSSelectorFromString(selectorStr); } NSArray<id<BHModuleProtocol>> *moduleInstances; if (target) { moduleInstances = @[target]; } else { moduleInstances = [self.BHModulesByEvent objectForKey:@(eventType)]; } [moduleInstances enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(id<BHModuleProtocol> moduleInstance, NSUInteger idx, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) { if ([moduleInstance respondsToSelector:seletor]) { #pragma clang diagnostic push #pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Warc-performSelector-leaks" [moduleInstance performSelector:seletor withObject:context]; #pragma clang diagnostic pop [[BHTimeProfiler sharedTimeProfiler] recordEventTime:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ --- %@", [moduleInstance class], NSStringFromSelector(seletor)]]; } }]; }
从上面的代码可以看出,事件类型分发是在方法handleModuleEvent:forTarget:withCustomParam:中进行。如之前所述,需要对BHMInitEvent 和BHMTearDownEvent 做特殊处理。同时,触发各个module(从self.BHModulesByEvent中获取)中的响应事件方法通过performSelector:withObject:来调用。
注意这里的module都是遵循BHModuleProtocol 协议的。
通用事件中,可以在modSetup 中设置环境变量,通过context.env 可以判断我们的应用环境状态来决定我们如何配置我们的应用。如下所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 -(void)modSetup:(BHContext *)context { switch (context.env) { case BHEnvironmentDev: //....初始化开发环境 break; case BHEnvironmentProd: //....初始化生产环境 default: break; } }
业务自定义事件
如果觉得系统事件、通用事件不足以满足需要,我们还将事件封装简化成BHAppdelgate,你可以通过继承 BHAppdelegate来扩展自己的事件。通过以下方式来注册自定义事件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 - (void)registerCustomEvent:(NSInteger)eventType withModuleInstance:(id)moduleInstance andSelectorStr:(NSString *)selectorStr { if (eventType < 1000) { return; } [self registerEvent:eventType withModuleInstance:moduleInstance andSelectorStr:selectorStr]; }
触发带参数的事件响应:
1 2 3 4 - (void)triggerEvent:(NSInteger)eventType withCustomParam:(NSDictionary *)customParam { [self handleModuleEvent:eventType forTarget:nil withCustomParam:customParam]; }
BeeHive模块注册
使用注解的方式注册Module和Service时,Module和Service的注册发生在加载镜像文件时期。
plist方式注册Module和Service,是在AppDelegate中设置BeeHive的Context时加载注册。
Module动态注册是在+load方法中,也是在加载镜像时注册。Service的动态注册可以Module的modInit:或者modSetup:中,或者使用时注册。
模块注册有三种方式:Annotation方式注册、读取本地plist方式注册、Load方法注册。所谓注册,就是将Module类告知BHModuleManager来管理。由此可见,在BeeHive中是通过BHModuleManager来管理各个模块的,BHModuleManager中只会管理已经被注册过的模块。
Annotation方式注册
通过BeeHiveMod宏进行Annotation标记。
BeeHiveMod宏定义如下:
1 2 #define BeeHiveMod(name) \ class BeeHive; char * k##name##_mod BeeHiveDATA(BeehiveMods) = ""#name"";
BeeHiveDATA也是一个宏:
1 #define BeeHiveDATA(sectname) __attribute((used, section("__DATA,"#sectname"")))
在预编译结束后,BeeHiveMode宏最终会完全展开成下面的样子:
1 @class BeeHive; char * kShopModule_mod __attribute((used, section("__DATA,""BeehiveMods"""))) = """ShopModule""";
这里需要注意双引号的总对数。
关于__attribute的用法,可参考我的另一篇attribute
__attribute第一个参数used ,它的作用是告诉编译器,我声明的这个符号是需要保留的。被used修饰以后,意味着即使函数没有被引用,在Release下也不会被优化。如果不加这个修饰,那么Release环境链接器会去掉没有被引用的段。
有时候我们需要指定一个特殊的段,来存放我们想要的数据。这里我们就把数据存在__DATA数据段里面的"BeehiveMods"section中。 Attributes的修饰关键字section ("section-name”)可以达到此要求。
上述代码中:
1 @class BeeHive; char * kShopModule_mod __attribute((used, section("__DATA,""BeehiveMods"""))) = """ShopModule""";
去掉__attribute的属性,相当于:
1 @class BeeHive; char * kShopModule_mod = """ShopModule""";
只不过是将kShopModule_mod 变量存储在了__DATA段的BeehiveMods section中。
这样,所有的Module类名的字符串都会放置在__DATA段BeehiveMods section中,那么如何取出这些字符串呢?
这里先介绍一下__attribute__((constructor)):
constructor :顾名思义,构造器加上这个属性的函数会在可执行文件(或 shared library)load时被调用,可以理解为在 main() 函数调用前执行:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 __attribute__((constructor)) static void beforeMain(void) { NSLog(@"beforeMain"); } __attribute__((destructor)) static void afterMain(void) { NSLog(@"afterMain"); } int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { NSLog(@"main"); return 0; } // Console: // "beforeMain" -> "main" -> “afterMain"
_dyld_register_func_for_add_image:这个函数是用来注册回调,当dyld链接符号时,调用此回调函数。在dyld加载镜像时,会执行注册过的回调函数;当然,我们也可以使用下面的方法注册自定义的回调函数,同时也会为所有已经加载的镜像执行回调:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 /* * The following functions allow you to install callbacks which will be called * by dyld whenever an image is loaded or unloaded. During a call to _dyld_register_func_for_add_image() * the callback func is called for every existing image. Later, it is called as each new image * is loaded and bound (but initializers not yet run). The callback registered with * _dyld_register_func_for_remove_image() is called after any terminators in an image are run * and before the image is un-memory-mapped. */ extern void _dyld_register_func_for_add_image(void (*func)(const struct mach_header* mh, intptr_t vmaddr_slide)) extern void _dyld_register_func_for_remove_image(void (*func)(const struct mach_header* mh, intptr_t vmaddr_slide))
对于每一个已经存在的镜像,当它被动态链接时,都会执行回调void (*func)(const struct mach_header* mh, intptr_t vmaddr_slide),传入文件的mach_header以及一个虚拟内存地址 intptr_t。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 __attribute__((constructor)) void initProphet() { _dyld_register_func_for_add_image(dyld_callback); } static void dyld_callback(const struct mach_header *mhp, intptr_t vmaddr_slide) { NSArray *mods = BHReadConfiguration(BeehiveModSectName, mhp); for (NSString *modName in mods) { Class cls; if (modName) { cls = NSClassFromString(modName); if (cls) { [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] registerDynamicModule:cls]; } } } } NSArray<NSString *>* BHReadConfiguration(char *sectionName,const struct mach_header *mhp) { NSMutableArray *configs = [NSMutableArray array]; unsigned long size = 0; #ifndef __LP64__ uintptr_t *memory = (uintptr_t*)getsectiondata(mhp, SEG_DATA, sectionName, &size); #else const struct mach_header_64 *mhp64 = (const struct mach_header_64 *)mhp; uintptr_t *memory = (uintptr_t*)getsectiondata(mhp64, SEG_DATA, sectionName, &size); #endif unsigned long counter = size/sizeof(void*); for(int idx = 0; idx < counter; ++idx){ char *string = (char*)memory[idx]; NSString *str = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:string]; if(!str)continue; BHLog(@"config = %@", str); if(str) [configs addObject:str]; } return configs; }
mach_header是定义在usr/include/mach-o/loader.h中的数据结构:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 /* * The 64-bit mach header appears at the very beginning of object files for * 64-bit architectures. */ struct mach_header_64 { uint32_t magic; /* mach magic number identifier */ cpu_type_t cputype; /* cpu specifier */ cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier */ uint32_t filetype; /* type of file */ uint32_t ncmds; /* number of load commands */ uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* the size of all the load commands */ uint32_t flags; /* flags */ uint32_t reserved; /* reserved */ };
通过调用BHReadConfiguration 函数,我们就可以拿到之前注册到BeehiveMods 特殊段里面的各个Module的类名,该函数返回类名字符串的数组。
然后将Module交由到BHModuleManager管理:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 - (void)registerDynamicModule:(Class)moduleClass { [self registerDynamicModule:moduleClass shouldTriggerInitEvent:NO]; } - (void)registerDynamicModule:(Class)moduleClass shouldTriggerInitEvent:(BOOL)shouldTriggerInitEvent { [self addModuleFromObject:moduleClass shouldTriggerInitEvent:shouldTriggerInitEvent]; } - (void)addModuleFromObject:(id)object shouldTriggerInitEvent:(BOOL)shouldTriggerInitEvent { Class class; NSString *moduleName = nil; if (object) { class = object; moduleName = NSStringFromClass(class); } else { return ; } /** 检测是否已存在Module类 */ __block BOOL flag = YES; [self.BHModules enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(id _Nonnull obj, NSUInteger idx, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) { if ([obj isKindOfClass:class]) { flag = NO; *stop = YES; } }]; if (!flag) { /**< 如果已存在,则返回,不做处理 */ return; } if ([class conformsToProtocol:@protocol(BHModuleProtocol)]) { NSMutableDictionary *moduleInfo = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary]; /** basicModuleLevel 这个方法如果不实现,Level是Normal: 1 */ BOOL responseBasicLevel = [class instancesRespondToSelector:@selector(basicModuleLevel)]; int levelInt = 1; if (responseBasicLevel) { /** basicModuleLevel 这个方法如果实现,Level是Basic: 0 */ levelInt = 0; } [moduleInfo setObject:@(levelInt) forKey:kModuleInfoLevelKey]; if (moduleName) { [moduleInfo setObject:moduleName forKey:kModuleInfoNameKey]; } [self.BHModuleInfos addObject:moduleInfo]; /** 初始化module实例 */ id<BHModuleProtocol> moduleInstance = [[class alloc] init]; [self.BHModules addObject:moduleInstance]; [moduleInfo setObject:@(YES) forKey:kModuleInfoHasInstantiatedKey]; /** 将module按照优先级排序 */ [self.BHModules sortUsingComparator:^NSComparisonResult(id<BHModuleProtocol> moduleInstance1, id<BHModuleProtocol> moduleInstance2) { NSNumber *module1Level = @(BHModuleNormal); NSNumber *module2Level = @(BHModuleNormal); if ([moduleInstance1 respondsToSelector:@selector(basicModuleLevel)]) { module1Level = @(BHModuleBasic); } if ([moduleInstance2 respondsToSelector:@selector(basicModuleLevel)]) { module2Level = @(BHModuleBasic); } if (module1Level.integerValue != module2Level.integerValue) { return module1Level.integerValue > module2Level.integerValue; } else { NSInteger module1Priority = 0; NSInteger module2Priority = 0; if ([moduleInstance1 respondsToSelector:@selector(modulePriority)]) { module1Priority = [moduleInstance1 modulePriority]; } if ([moduleInstance2 respondsToSelector:@selector(modulePriority)]) { module2Priority = [moduleInstance2 modulePriority]; } return module1Priority < module2Priority; } }]; /** 给module注册事件 */ [self registerEventsByModuleInstance:moduleInstance]; if (shouldTriggerInitEvent) { [self handleModuleEvent:BHMSetupEvent forTarget:moduleInstance withSeletorStr:nil andCustomParam:nil]; [self handleModulesInitEventForTarget:moduleInstance withCustomParam:nil]; dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ [self handleModuleEvent:BHMSplashEvent forTarget:moduleInstance withSeletorStr:nil andCustomParam:nil]; }); } } }
所有需要注册的Module必须遵循BHModuleProtocol 协议,否则不会被存储。
读取本地Plist方式注册
首先需要设置本地Plist文件的读取路径:
1 [BHContext shareInstance].moduleConfigName = @"BeeHive.bundle/BeeHive";//可选,默认为BeeHive.bundle/BeeHive.plist
BeeHive的所有配置都可以通过BHContext进行传递。
Plist文件的字段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd"> <plist version="1.0"> <dict> <key>URLGlobalScheme</key> <string>com.alibaba.beehive</string> <key>moduleClasses</key> <array> <dict> <key>moduleClass</key> <string>HomeModule</string> <key>moduleLevel</key> <integer>1</integer> <key>modulePriority</key> <string>600</string> </dict> <dict> <key>moduleClass</key> <string>TMTradeAdapter</string> <key>moduleLevel</key> <integer>1</integer> <key>modulePriority</key> <string>599</string> </dict> </array> </dict> </plist>
在AppDelegate中 [[BeeHive shareInstance] setContext:[BHContext shareInstance]]; 设置BHContext时就会注册plist中的module。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 - (void)loadLocalModules { NSString *plistPath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:[BHContext shareInstance].moduleConfigName ofType:@"plist"]; if (![[NSFileManager defaultManager] fileExistsAtPath:plistPath]) { return; } NSDictionary *moduleList = [[NSDictionary alloc] initWithContentsOfFile:plistPath]; NSArray<NSDictionary *> *modulesArray = [moduleList objectForKey:kModuleArrayKey]; NSMutableDictionary<NSString *, NSNumber *> *moduleInfoByClass = @{}.mutableCopy; [self.BHModuleInfos enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(NSDictionary * _Nonnull obj, NSUInteger idx, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) { [moduleInfoByClass setObject:@1 forKey:[obj objectForKey:kModuleInfoNameKey]]; }]; [modulesArray enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(NSDictionary * _Nonnull obj, NSUInteger idx, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) { if (!moduleInfoByClass[[obj objectForKey:kModuleInfoNameKey]]) { [self.BHModuleInfos addObject:obj]; } }]; }
将Plist中的module加入到BHModuleInfos 中。
Load方法注册
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 // BeeHive + (void)load { [BeeHive registerDynamicModule:[self class]]; } + (void)registerDynamicModule:(Class)moduleClass { [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] registerDynamicModule:moduleClass]; } // BHModuleManager - (void)registerDynamicModule:(Class)moduleClass { [self registerDynamicModule:moduleClass shouldTriggerInitEvent:NO]; }
Load方法最终是调用BHModuleManager中的registerDynamicModule:方法来处理,该方法已在上一节中说明。
+load的方式可以使用BH_EXPORT_MODULE 宏来替代完成。
1 2 3 #define BH_EXPORT_MODULE(isAsync) \ + (void)load { [BeeHive registerDynamicModule:[self class]]; } \ -(BOOL)async { return [[NSString stringWithUTF8String:#isAsync] boolValue];}
在BH_EXPORT_MODULE 宏中传入了参数isAsync ,代表是否异步加载Module模块。如果是YES,则表示需要异步加载,NO则表示同步加载。
回过头来看看AppDelegate中setContext方法中的操作:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 // AppDelegate [[BeeHive shareInstance] setContext:[BHContext shareInstance]]; // BeeHive -(void)setContext:(BHContext *)context { _context = context; static dispatch_once_t onceToken; dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{ [self loadStaticServices]; [self loadStaticModules]; }); } - (void)loadStaticModules { [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] loadLocalModules]; [[BHModuleManager sharedManager] registedAllModules]; }
重点关注一下registedAllModules方法 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 - (void)registedAllModules { /** 按照优先级从大到小顺序排列 */ [self.BHModuleInfos sortUsingComparator:^NSComparisonResult(NSDictionary *module1, NSDictionary *module2) { NSNumber *module1Level = (NSNumber *)[module1 objectForKey:kModuleInfoLevelKey]; NSNumber *module2Level = (NSNumber *)[module2 objectForKey:kModuleInfoLevelKey]; if (module1Level.integerValue != module2Level.integerValue) { return module1Level.integerValue > module2Level.integerValue; } else { NSNumber *module1Priority = (NSNumber *)[module1 objectForKey:kModuleInfoPriorityKey]; NSNumber *module2Priority = (NSNumber *)[module2 objectForKey:kModuleInfoPriorityKey]; return module1Priority.integerValue < module2Priority.integerValue; } }]; NSMutableArray *tmpArray = [NSMutableArray array]; //module init:初始化所有的module [self.BHModuleInfos enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(NSDictionary *module, NSUInteger idx, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) { NSString *classStr = [module objectForKey:kModuleInfoNameKey]; Class moduleClass = NSClassFromString(classStr); BOOL hasInstantiated = ((NSNumber *)[module objectForKey:kModuleInfoHasInstantiatedKey]).boolValue; if (NSStringFromClass(moduleClass) && !hasInstantiated) { id<BHModuleProtocol> moduleInstance = [[moduleClass alloc] init]; [tmpArray addObject:moduleInstance]; } }]; // [self.BHModules removeAllObjects]; [self.BHModules addObjectsFromArray:tmpArray]; //给module对象注册系统事件 [self registerAllSystemEvents]; }
在经历registedAllModules方法之后,所有注册的module都生成了对应的实例对象。
注意:
所有的Module的对象都要是遵守BHModuleProtocol 协议的。
Module不能在任何其他地方alloc创建出来,即使创建一个新的Module实例出来,它也并不在BHModuleManager的管理下,无法接收BHModuleManager分发的系统事件。
BeeHive模块间调用
通过处理Event编写各个业务模块可以实现插件化编程,各业务模块之间没有任何依赖,core与module之间通过event交互,实现了插件隔离。但有时候我们需要模块间的相互调用某些功能来协同完成功能。目前模块间的调用使用基于接口的实现Service访问方式(Java spring框架实现)。基于接口Service访问的优点是可以编译时检查发现接口的变更,从而及时修正接口问题。缺点是需要依赖接口定义的头文件,通过模块增加得越多,维护接口定义的也有一定工作量。
模块间调用的协议都是通过BHServiceManager来维护的。
BeeHive提供了三种方式来注册协议,这里和module的注册方式相同:Annotation方式注册、读取本地plist方式注册、API注册。
Annotation方式注册
使用@BeeHiveService进行Annotation标记。BeeHiveService的宏定义如下:
1 2 3 4 #define BeeHiveService(servicename,impl) \ class BeeHive; char * k##servicename##_service BeeHiveDATA(BeehiveServices) = "{ \""#servicename"\" : \""#impl"\"}"; #define BeeHiveDATA(sectname) __attribute((used, section("__DATA,"#sectname"")))
在示例中,@BeeHiveService(HomeServiceProtocol,BHViewController)在预编译结束后会完全展开成如下所示:
1 @class BeeHive; char * kHomeServiceProtocol_service __attribute((used, section("__DATA,""BeehiveServices"""))) = "{ \"""HomeServiceProtocol""\" : \"""BHViewController""\"}”;
这里类比注册module时的Annotation解析,也是把数据存在特殊的段内,具体的原理可以参考注册module的分析。
同理,通过调用函数BHReadConfiguration读取之前注册到特殊段BeehiveServices 中的数据,这里是如下所示的json字符串,{协议字符串:实现该协议的class类名字符串} ,如下所示:
{"HomeServiceProtocol":"BHViewController”}
读取到数据后,进行service的注册:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 static void dyld_callback(const struct mach_header *mhp, intptr_t vmaddr_slide) { //register module ... //register services NSArray<NSString *> *services = BHReadConfiguration(BeehiveServiceSectName,mhp); for (NSString *map in services) { NSData *jsonData = [map dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]; NSError *error = nil; id json = [NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:jsonData options:0 error:&error]; if (!error) { if ([json isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]] && [json allKeys].count) { NSString *protocol = [json allKeys][0]; NSString *clsName = [json allValues][0]; if (protocol && clsName) { [[BHServiceManager sharedManager] registerService:NSProtocolFromString(protocol) implClass:NSClassFromString(clsName)]; } } } } } - (void)registerService:(Protocol *)service implClass:(Class)implClass { NSParameterAssert(service != nil); NSParameterAssert(implClass != nil); if (![implClass conformsToProtocol:service]) { if (self.enableException) { @throw [NSException exceptionWithName:NSInternalInconsistencyException reason:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ module does not comply with %@ protocol", NSStringFromClass(implClass), NSStringFromProtocol(service)] userInfo:nil]; } return; } //协议是否已经注册 if ([self checkValidService:service]) { if (self.enableException) { @throw [NSException exceptionWithName:NSInternalInconsistencyException reason:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ protocol has been registed", NSStringFromProtocol(service)] userInfo:nil]; } return; } NSString *key = NSStringFromProtocol(service); NSString *value = NSStringFromClass(implClass); if (key.length > 0 && value.length > 0) { [self.lock lock]; [self.allServicesDict addEntriesFromDictionary:@{key:value}]; [self.lock unlock]; } }
在注册协议前会有两个检查registerService:implClass::
检查implClass是否遵循了service
检查service协议是否已经注册
如果两个条件有一个没有检查通过,则会抛出异常。
如果条件通过,则会在allServicesDict 中加入键值对,{NSStringFromProtocol(service):NSStringFromClass(implClass)}
读取本地Plist方式注册
读取本地的plist文件之前,需要先设置plist文件路径。
1 2 //AppDelegate.m [BHContext shareInstance].serviceConfigName = @"BeeHive.bundle/BHService”;
BeeHive的配置都可以通过BHContext进行传递。
plist中的数据格式如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd"> <plist version="1.0"> <array> <dict> <key>service</key> <string>UserTrackServiceProtocol</string> <key>impl</key> <string>BHUserTrackViewController</string> </dict> </array> </plist>
注册plist中service的时机同注册plist管理的module类似:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 // AppDelegate.m - (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions { [BHContext shareInstance].application = application; [BHContext shareInstance].launchOptions = launchOptions; [BHContext shareInstance].moduleConfigName = @"BeeHive.bundle/BeeHive";//可选,默认为BeeHive.bundle/BeeHive.plist [BHContext shareInstance].serviceConfigName = @"BeeHive.bundle/BHService"; [BeeHive shareInstance].enableException = YES; [[BeeHive shareInstance] setContext:[BHContext shareInstance]]; [[BHTimeProfiler sharedTimeProfiler] recordEventTime:@"BeeHive::super start launch"]; [super application:application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:launchOptions]; ... return YES; } // BeeHive.m -(void)setContext:(BHContext *)context { _context = context; static dispatch_once_t onceToken; dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{ [self loadStaticServices]; [self loadStaticModules]; }); } -(void)loadStaticServices { [BHServiceManager sharedManager].enableException = self.enableException; [[BHServiceManager sharedManager] registerLocalServices]; }
注册service的具体实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 - (void)registerLocalServices { NSString *serviceConfigName = [BHContext shareInstance].serviceConfigName; NSString *plistPath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:serviceConfigName ofType:@"plist"]; if (!plistPath) { return; } NSArray *serviceList = [[NSArray alloc] initWithContentsOfFile:plistPath]; [self.lock lock]; for (NSDictionary *dict in serviceList) { NSString *protocolKey = [dict objectForKey:@"service"]; NSString *protocolImplClass = [dict objectForKey:@"impl"]; if (protocolKey.length > 0 && protocolImplClass.length > 0) { [self.allServicesDict addEntriesFromDictionary:@{protocolKey:protocolImplClass}]; } } [self.lock unlock]; }
注册完成之后,allServicesDict 中的值如下:
1 {@"HomeServiceProtocol" : @"BHViewController", @"UserTrackServiceProtocol" : @"BHUserTrackViewController"}
注意: NSString *plistPath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:serviceConfigName ofType:@"plist”]; 这段代码,如果主工程Podfile中未使用了use_frameworks!,则可以正常获取到plist,如果使用了use_frameworks!,则得使用其他方式获取,具体的方案请google。
API注册
API注册service使用的api是BeeHive的接口- (void)registerService:(Protocol *)proto service:(Class)serviceClass, 该接口内部实现也是调用BHServiceManager的registerService:implClass:接口。
1 2 3 4 // BeeHive.m - (void)registerService:(Protocol *)proto service:(Class)serviceClass { [[BHServiceManager sharedManager] registerService:proto implClass:serviceClass]; }
例如:[[BeeHive shareInstance] registerService:@protocol(TradeServiceProtocol) service:[BHTradeViewController class]];, 该代码可以放置在module的 modInit:方法内部或者modSetup:方法内部,具体可以查看使用文档或者demo。
注意:BHMSetupEvent 和BHMInitEvent 事件都会在项目的- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions函数内部触发。
BHServiceManager中的allServicesDict 包含了所有方式注册的service。
与module注册相比,service的注册没有对实现协议的对象进行初始化。只是将协议和实现协议的对象之间的这种关联关系存储和维护,而在module的注册过程中,对所有注册的module进行实例的初始化。
因此,在BHServiceManager的公共接口中,有一组createService:接口用于访问实现协议的对象。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 - (id)createService:(Protocol *)service { return [self createService:service withServiceName:nil]; } - (id)createService:(Protocol *)service withServiceName:(NSString *)serviceName { return [self createService:service withServiceName:serviceName shouldCache:YES]; } - (id)createService:(Protocol *)service withServiceName:(NSString *)serviceName shouldCache:(BOOL)shouldCache { if (!serviceName.length) { serviceName = NSStringFromProtocol(service); } id implInstance = nil; if (![self checkValidService:service]) { if (self.enableException) { @throw [NSException exceptionWithName:NSInternalInconsistencyException reason:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ protocol does not been registed", NSStringFromProtocol(service)] userInfo:nil]; } } NSString *serviceStr = serviceName; if (shouldCache) { id protocolImpl = [[BHContext shareInstance] getServiceInstanceFromServiceName:serviceStr]; if (protocolImpl) { return protocolImpl; } } Class implClass = [self serviceImplClass:service]; if ([[implClass class] respondsToSelector:@selector(singleton)]) { if ([[implClass class] singleton]) { if ([[implClass class] respondsToSelector:@selector(shareInstance)]) implInstance = [[implClass class] shareInstance]; else implInstance = [[implClass alloc] init]; if (shouldCache) { [[BHContext shareInstance] addServiceWithImplInstance:implInstance serviceName:serviceStr]; return implInstance; } else { return implInstance; } } } return [[implClass alloc] init]; }
从上面的实现中可以看出:
service对象存在单例和多实例的区别。
如果BHServiceProtocol 协议对象实现了singleton返回YES,且shouldCache 入参值是YES,则通过createService:获取的对象为单例对象,如果singleton方法返回的是NO,则每次调用createService:都会创建一个新的对象。
这里的单例存在线程安全问题。如果开发者将BHServiceProtocol 协议对象实现了singleton返回YES,且shareInstance方法的实现是返回单例对象,则不管shouldCache 的入参值是YES还是NO,createService:都会是同一个实例。但是,如果开发者将shareInstance方法的实现只是返回对象(非单例),即使singleton返回YES,shouldCache 入参值是YES,也可能存在多个实例的情况。
上下文环境Context
BeeHive中使用BHContext初始化设置应用的项目信息,并在各模块间共享整个应用程序的信息。例如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 - (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions { [BHContext shareInstance].env = BHEnvironmentDev; //定义应用的运行开发环境 [BHContext shareInstance].application = application; [BHContext shareInstance].launchOptions = launchOptions; [BHContext shareInstance].moduleConfigName = @"BeeHive.bundle/CustomModulePlist";//可选,默认为BeeHive.bundle/BeeHive.plist [BHContext shareInstance].serviceConfigName = @"BeeHive.bundle/CustomServicePlist";//可选,默认为BeeHive.bundle/BHService.plist [[BeeHive shareInstance] setContext:[BHContext shareInstance]]; [super application:application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:launchOptions]; ... return YES; } //BHContext.h @interface BHContext : NSObject <NSCopying> //global env @property(nonatomic, assign) BHEnvironmentType env; //global config @property(nonatomic, strong) BHConfig *config; //application appkey @property(nonatomic, strong) NSString *appkey; //customEvent>=1000 @property(nonatomic, assign) NSInteger customEvent; @property(nonatomic, strong) UIApplication *application; @property(nonatomic, strong) NSDictionary *launchOptions; @property(nonatomic, strong) NSString *moduleConfigName; @property(nonatomic, strong) NSString *serviceConfigName; //3D-Touch model #if __IPHONE_OS_VERSION_MAX_ALLOWED > 80400 @property (nonatomic, strong) BHShortcutItem *touchShortcutItem; #endif //OpenURL model @property (nonatomic, strong) BHOpenURLItem *openURLItem; //Notifications Remote or Local @property (nonatomic, strong) BHNotificationsItem *notificationsItem; //user Activity Model @property (nonatomic, strong) BHUserActivityItem *userActivityItem; //watch Model @property (nonatomic, strong) BHWatchItem *watchItem; //custom param @property (nonatomic, copy) NSDictionary *customParam; @end
应用的运行开发环境
应用启动信息:application,launchOptions
module和service的plist配置信息
缓存的service
3D-Touch, OpenURL moduel, Remote Or Local Notifications, User Activity Model等
最后,附一张BeeHive主要类的的类图关系。
如果觉得本文对你有帮助,就请用微信随意打赏我吧^_^
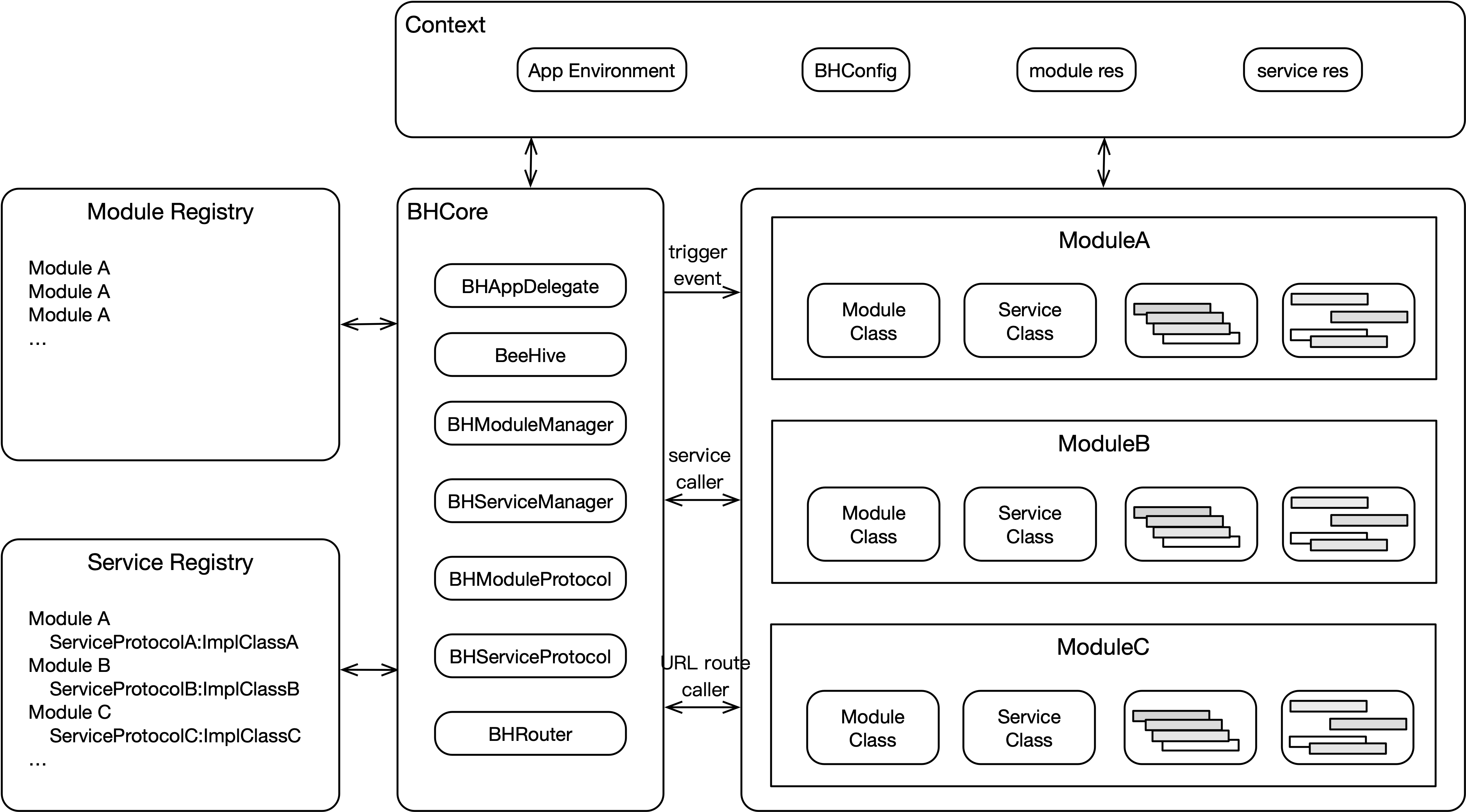 BeeHive架构图
BeeHive架构图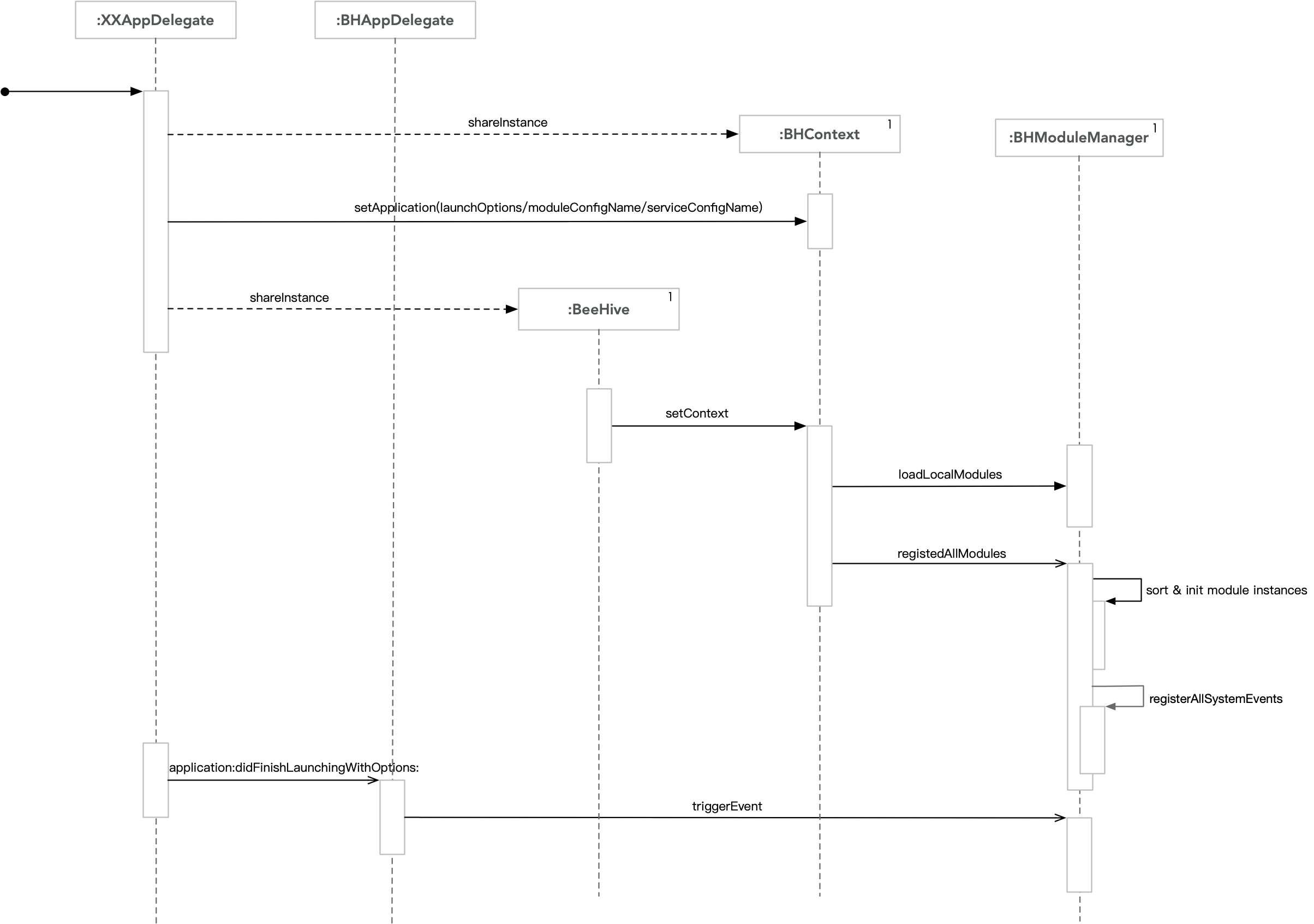 Module注册
Module注册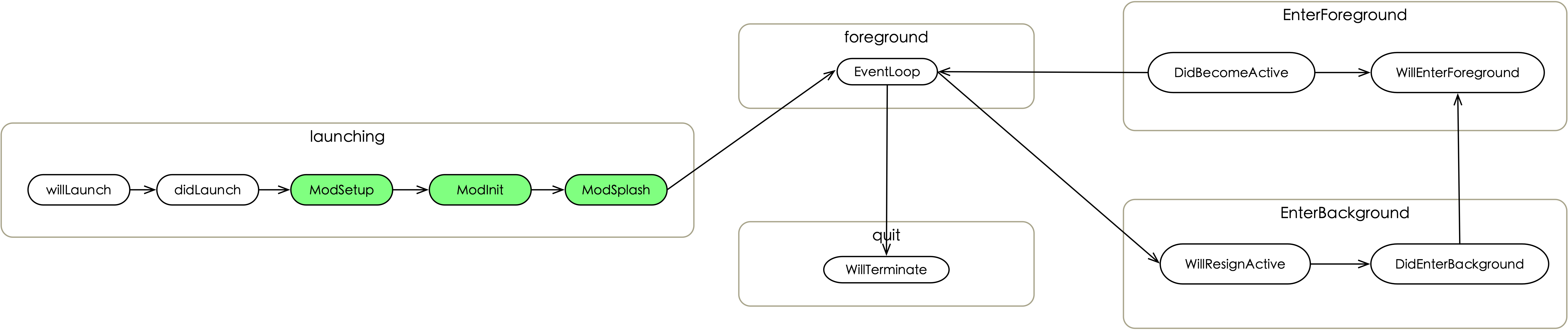 BeeHive事件扩展
BeeHive事件扩展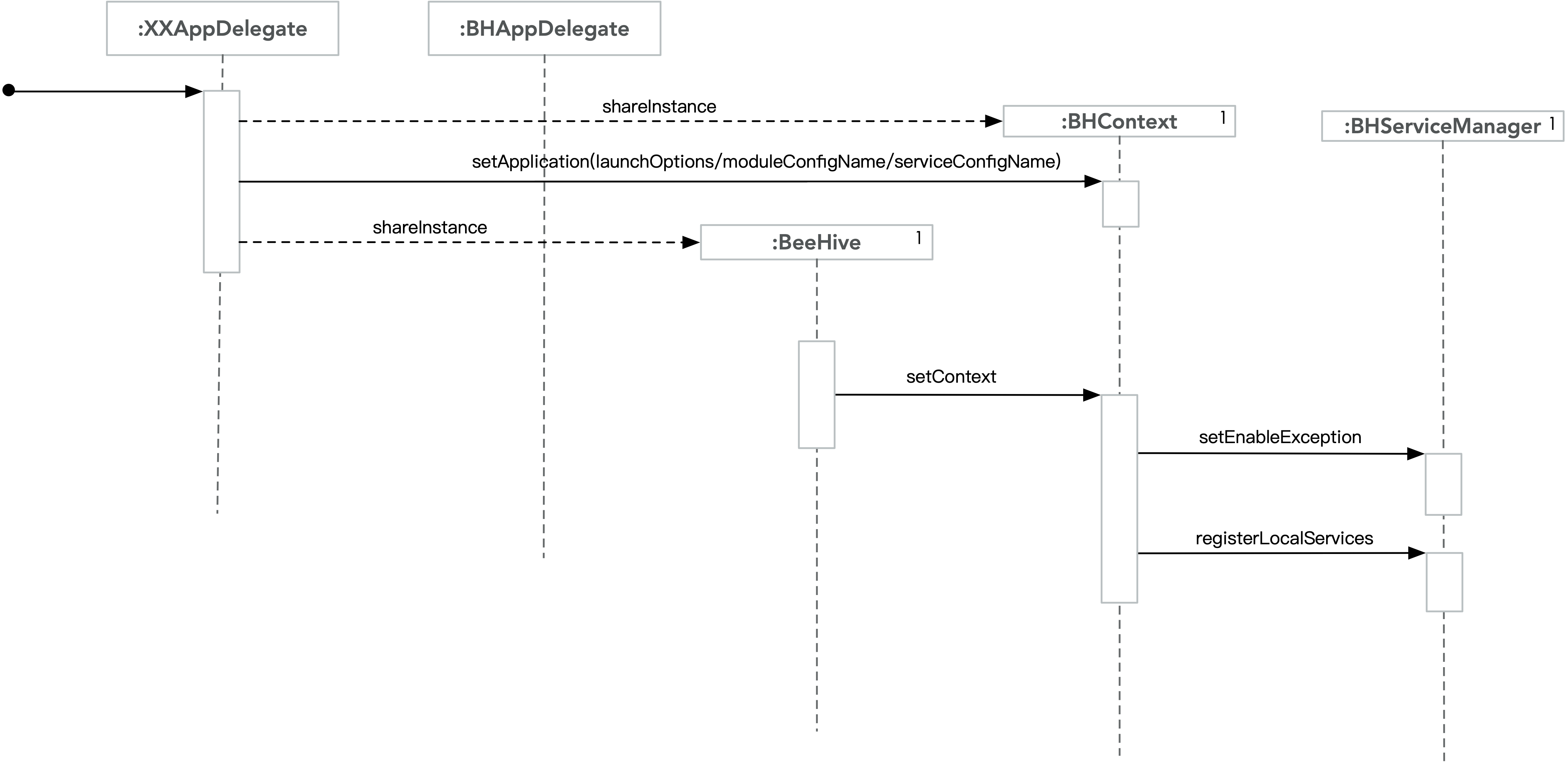 注册静态plist service
注册静态plist service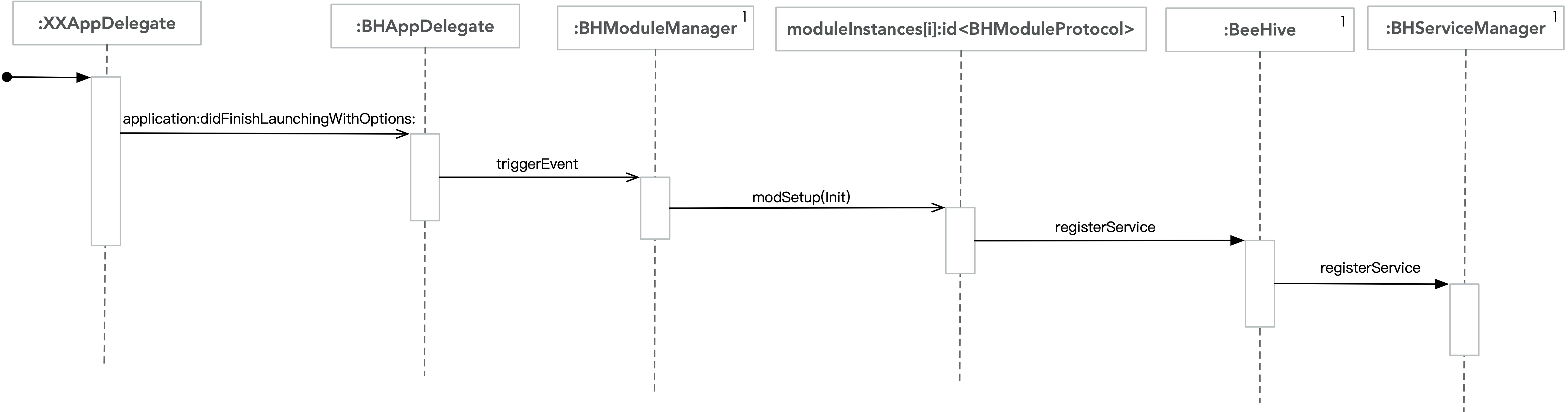 动态注册service
动态注册service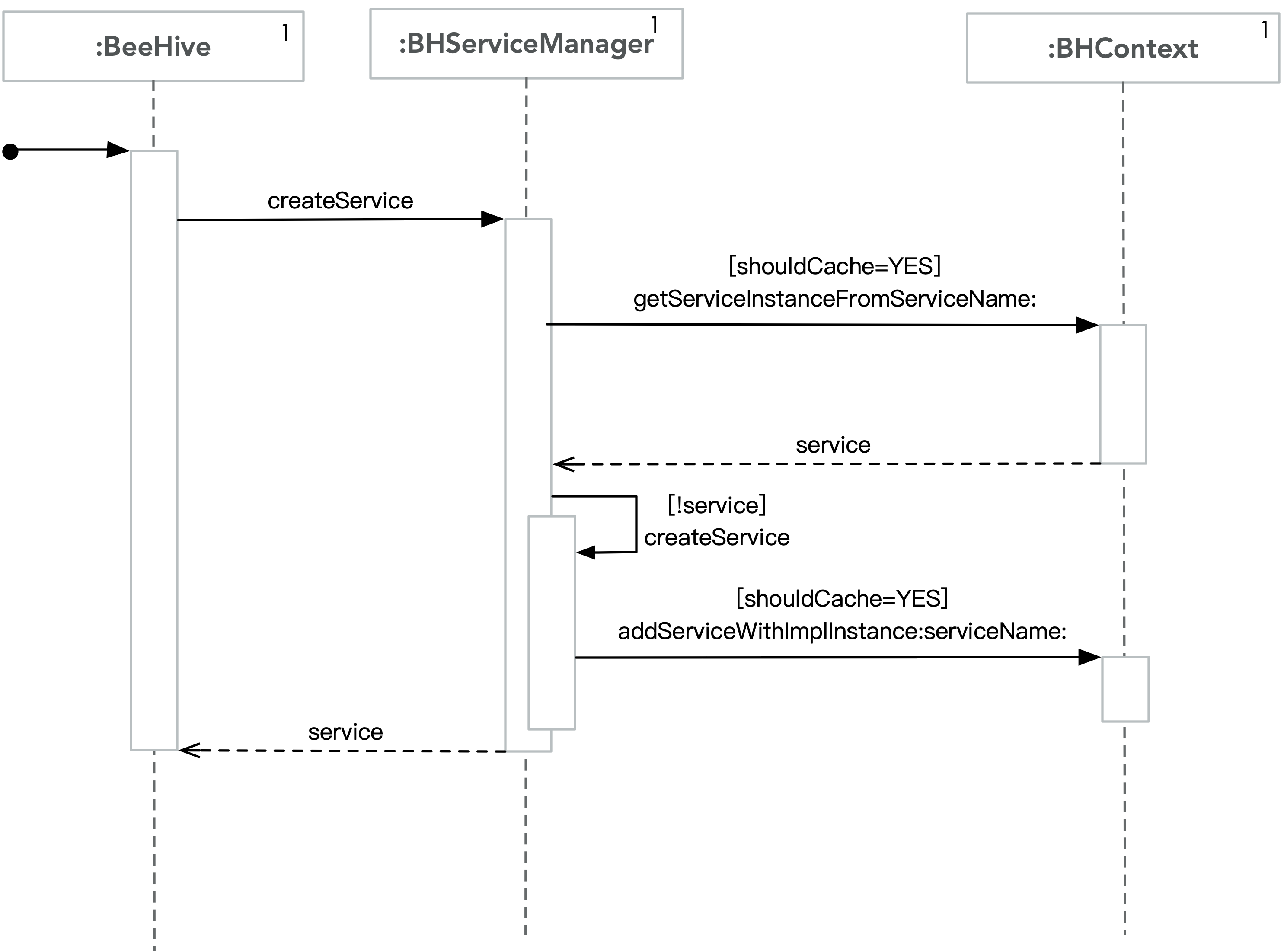 创建service实例
创建service实例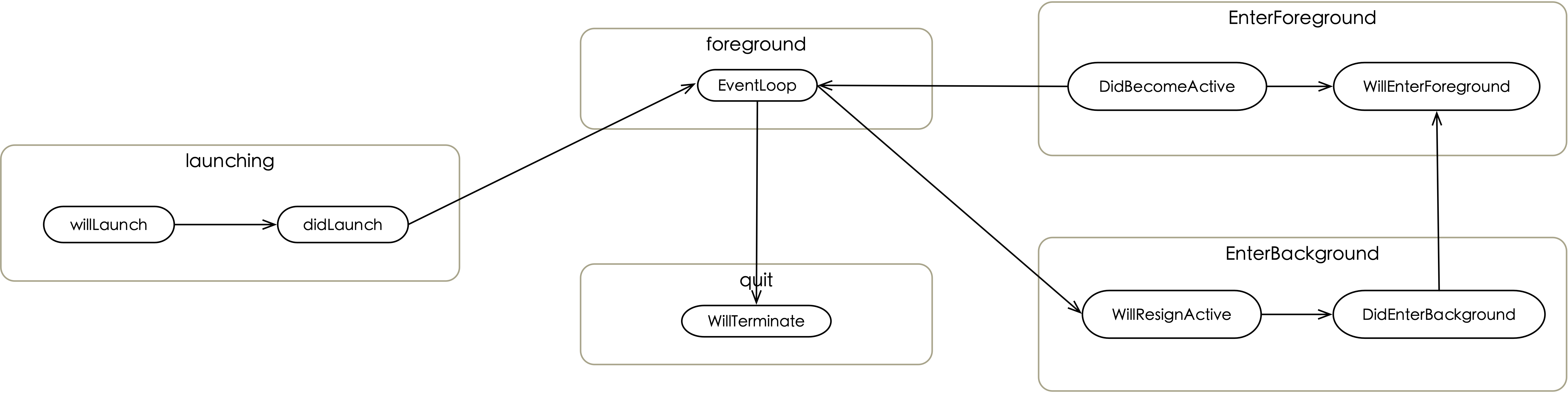 BeeHive系统事件
BeeHive系统事件 BeeHive通用事件
BeeHive通用事件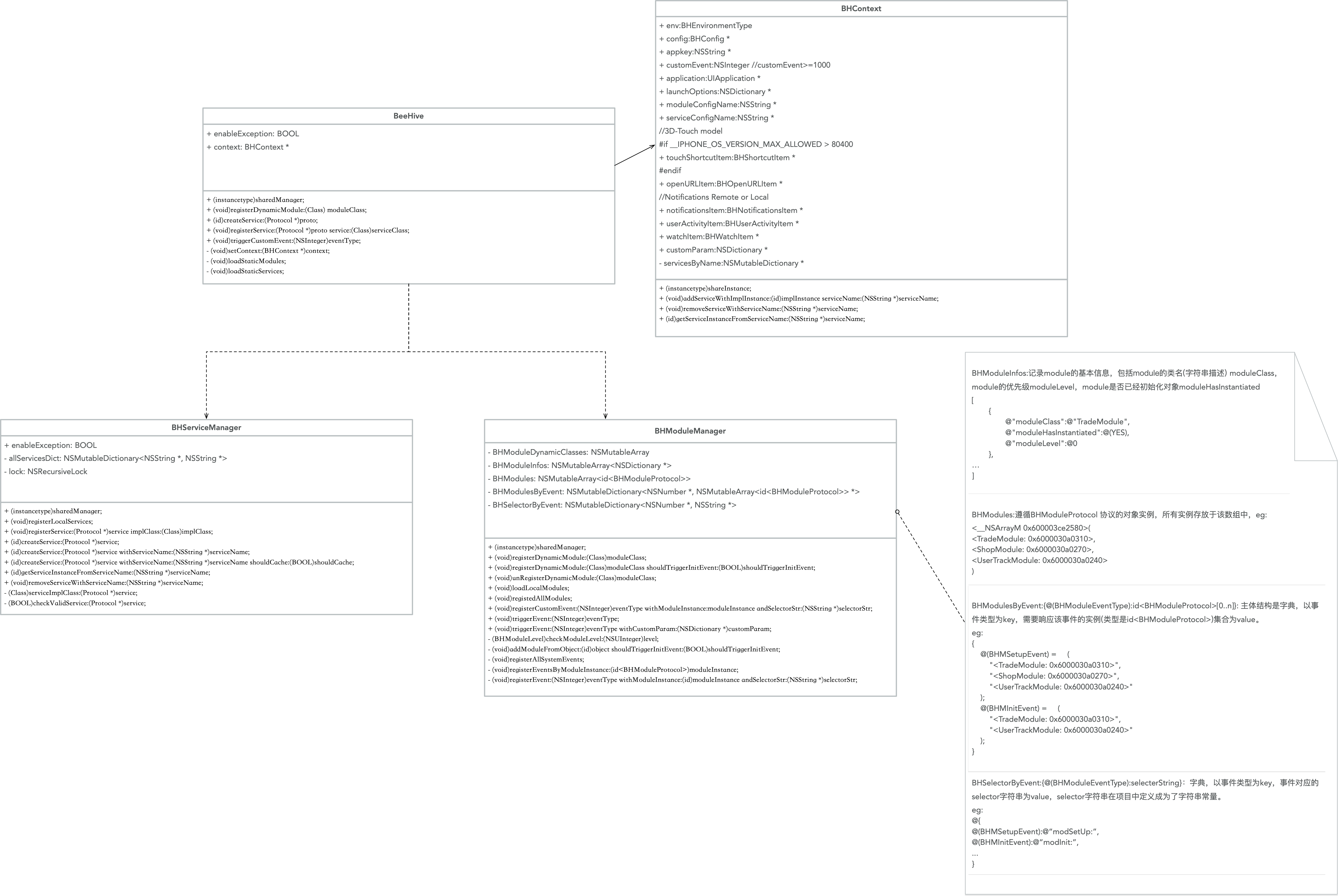 BeeHive类图
BeeHive类图
